If you’ve been on the lookout for the best diet plan for muscle gain, you’re in the right place. For health-conscious adults like us, seeking natural wellness while building muscle can feel overwhelming. I’ve been there, combing through endless contradictory advice and trying to separate the hype from what’s truly effective. That’s why I’ve put together this comprehensive guide—to give you a clear, scientifically-backed roadmap to gaining lean muscle naturally and sustainably.
In this long-form article, we’ll cover everything from the fundamentals of muscle growth, the importance of macronutrient balance, meal timing strategies, and hydration tips, to nutrient-dense food choices and smart supplementation. Whether you’re a beginner or simply aiming to boost your muscle gains without relying on quick fixes, this guide articulates actionable steps you can follow daily. Along the way, I’ll incorporate natural wellness principles to ensure your approach doesn’t just build muscle but also supports overall health.
Ready to dive into the best diet plan for muscle gain? Let’s go!
Understanding Muscle Growth and Nutrition Fundamentals
When it comes to muscle gain, understanding how your body actually builds muscle tissue is the cornerstone of nutrition planning.
How Muscle Protein Synthesis Drives Muscle Gain
Muscle protein synthesis (MPS) is the process where your body repairs and builds new muscle tissue after exercise. Think of it as your body’s construction crew—constantly breaking down old or damaged muscle proteins and replacing them with new ones, provided it has the right materials.
To support MPS, you require an adequate intake of quality protein throughout the day. Simply working out isn’t enough; your muscles need building blocks from protein-rich foods to grow stronger and bigger.
Interestingly, MPS spikes after resistance training and lasts for about 24-48 hours, making your nutrition both before and after workouts critically important. Also, consuming sufficient calories overall ensures your body has energy to fuel this process instead of breaking down muscle for energy.
Importance of a Caloric Surplus for Lean Muscle Mass
Here’s the deal: To gain muscle, you must eat more calories than your body burns—this is known as a caloric surplus. Without it, your body lacks the energy required to build muscle effectively. But it’s not just about overeating; the surplus needs to be controlled to promote lean muscle growth rather than fat gain.
From experience and research, a surplus of about 250-500 calories daily is generally ideal for most people. This range supports muscle hypertrophy (growth) with minimal fat gain. Tracking your calories — either via apps or journaling — and adjusting depending on your weekly weight and strength progress helps fine-tune this balance.
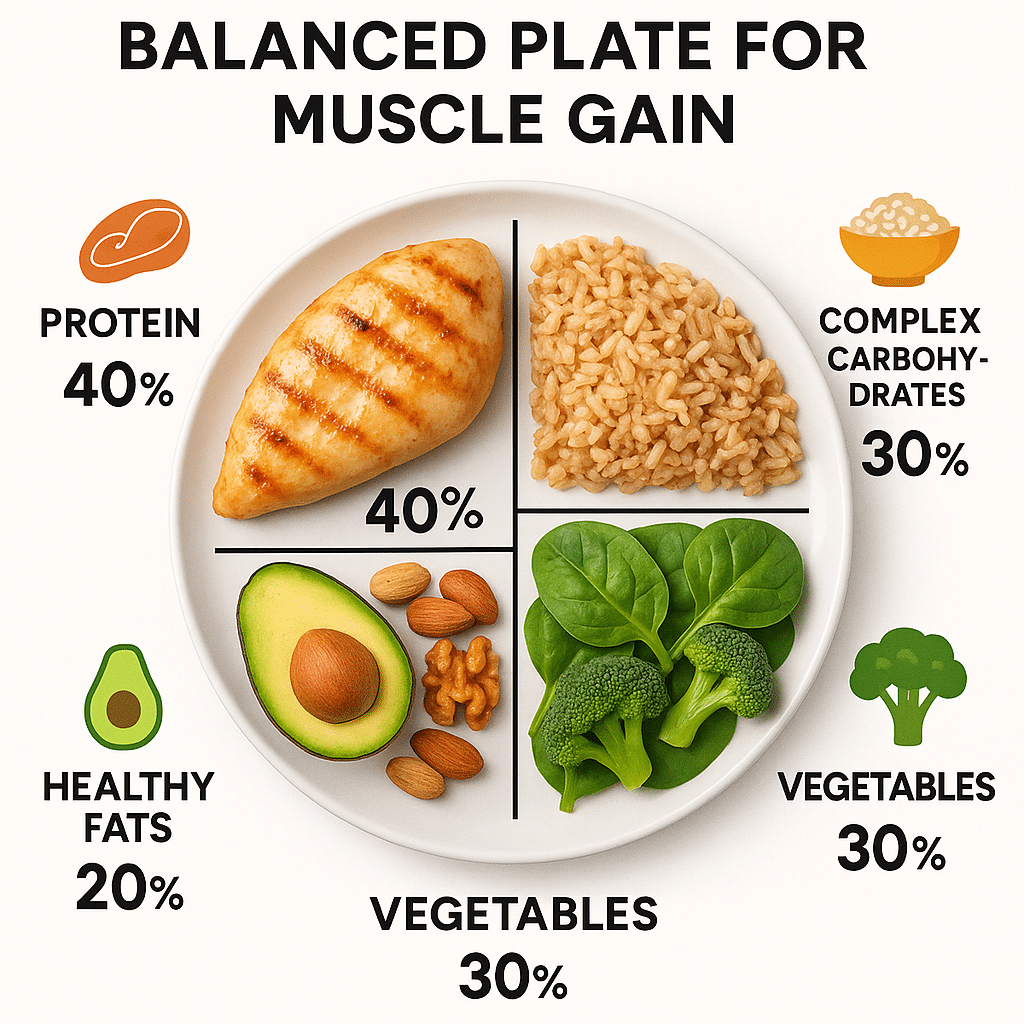
Macronutrient Ratios for Optimal Muscle Building
Balancing macros—the amounts of protein, carbohydrates, and fats—is key to building muscle efficiently while maintaining health.
Protein Intake: Amounts and Quality Sources
Protein is king when it comes to muscle building. The optimal protein consumption for muscle growth typically ranges between 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight daily. So, if you weigh 70 kg (about 154 lbs), aim for around 112–154 grams of protein daily.
Quality matters. Animal sources such as chicken, turkey, lean beef, fish, eggs, and dairy contain all essential amino acids necessary for muscle repair and growth. For those interested in plant-based options, combining legumes, grains, nuts, and seeds can provide a complete amino acid profile. Brands like Orgain Organic Plant-Based Protein offer excellent plant protein powders that support muscle gains naturally.
Carbohydrate Needs for Energy and Muscle Recovery
Carbohydrates fuel your workouts and replenish glycogen stores in muscles after training. A calorie surplus diet plan for muscle growth often includes moderate to high carbohydrate consumption, particularly around training times.
Complex carbs like oats, brown rice, quinoa, sweet potatoes, and legumes release energy slowly and support sustained performance. During intense training phases, ensure carbohydrates make up about 40–60% of your daily calories.
Healthy Fats: Hormone Production and Overall Wellness
Don’t skimp on fats—they’re vital for hormone production, including testosterone, which influences muscle building. Healthy fats also support brain function and reduce inflammation.
Include sources like avocados, olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish such as salmon. Aim for fats to provide about 20–30% of your daily caloric intake, focusing on omega-3 fatty acids for their anti-inflammatory benefits.
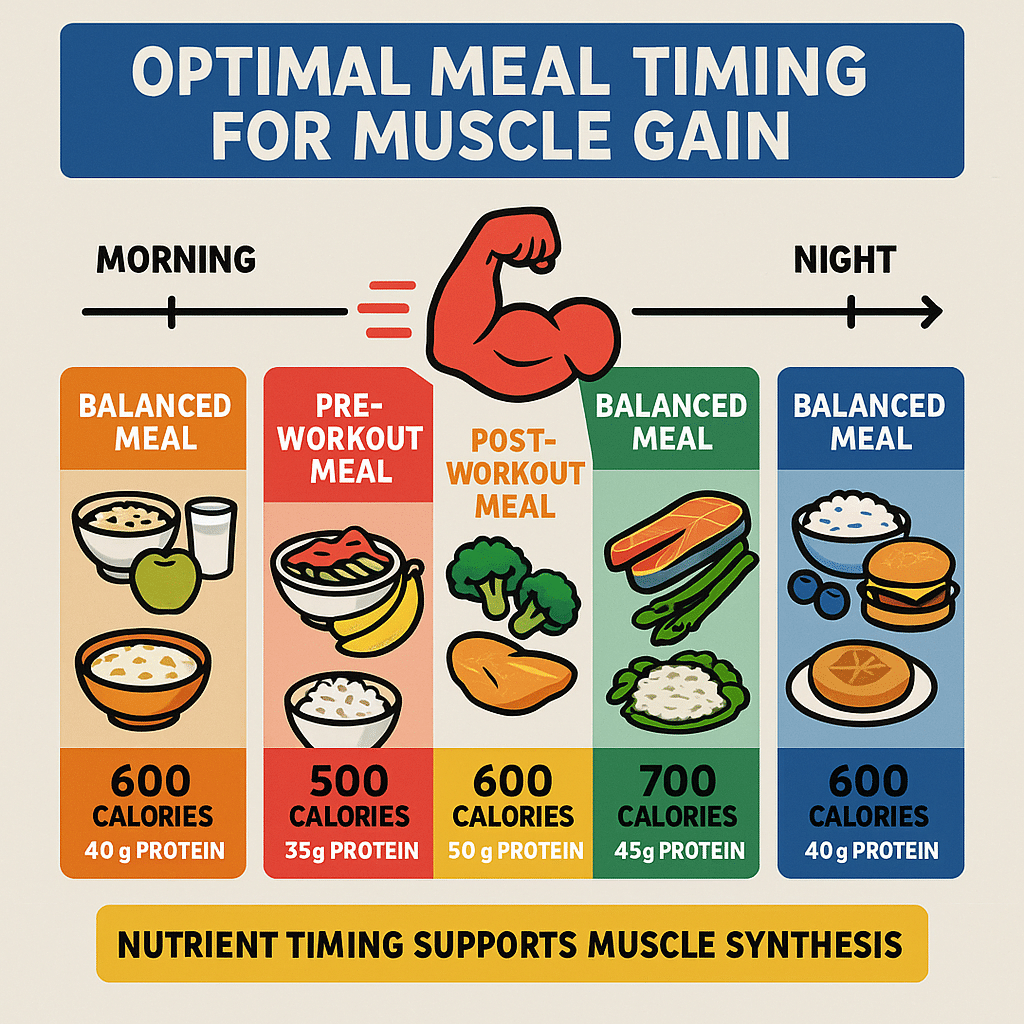
Meal Timing and Frequency Strategies for Muscle Hypertrophy
The way you distribute your meals can impact muscle gain by optimizing nutrient delivery and recovery.
Pre-Workout and Post-Workout Nutrition
Eating strategically around your workouts supports performance and recovery. Before a workout, consuming a balanced meal with protein and carbs about 1-2 hours prior provides energy.
After training, the anabolic window post-workout—while a bit broader than once believed—is still the prime time to eat protein and carbs to kickstart MPS and glycogen restoration. For example, a shake with whey protein and a banana works wonders.
Distributing Protein Across Multiple Meals Daily
Studies show spreading protein intake evenly across 3-6 meals or snacks maximizes MPS throughout the day better than consuming most protein at one or two meals. Aiming for 20-40 grams of protein per meal supports continuous muscle repair.
Hydration’s Role in Muscle Performance and Recovery
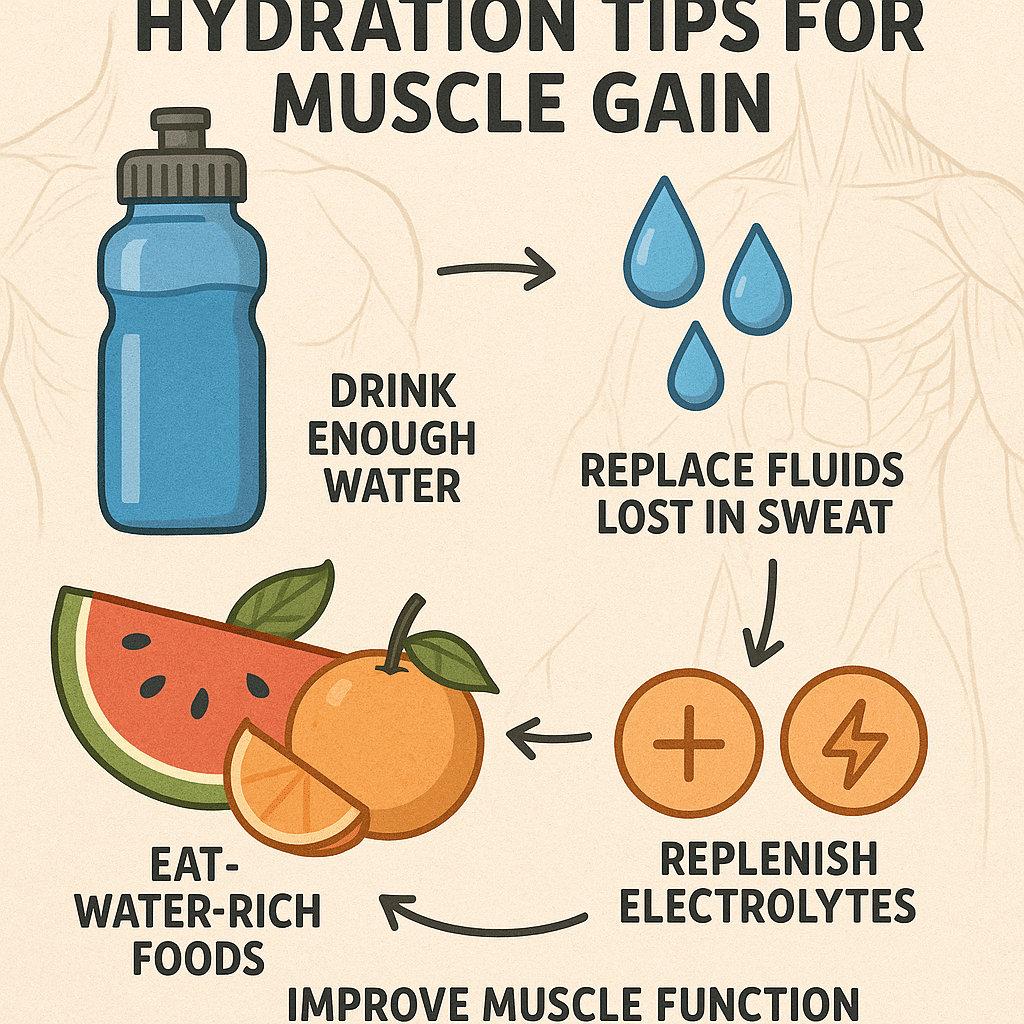
Hydration often flies under the radar but is critical for muscle function.
Guidelines for Daily Fluid Intake and Electrolyte Balance
Water plays a vital role in nutrient transport, joint lubrication, and muscle contractions. Dehydration impairs strength and recovery.
General recommendations suggest drinking at least 3 liters per day, more if you sweat heavily during workouts. Including electrolyte-rich beverages or foods—such as coconut water or foods with potassium (bananas) and magnesium (spinach)—helps maintain balance.
Nutrient-Dense Foods That Maximize Muscle Growth Naturally
Choosing whole, nutrient-dense foods ensures you get necessary vitamins and minerals that support overall health and muscle growth.
Lean Protein Choices: Animal and Plant-Based Options
Lean chicken breast, turkey, lean cuts of beef, Greek yogurt, eggs, tofu, tempeh, lentils, and cottage cheese are excellent picks. Variety not only prevents diet fatigue but also offers a wider nutrient spectrum.
Complex Carbohydrates to Fuel Training and Recovery
Opt for sweet potatoes, brown rice, whole wheat pasta, quinoa, and legumes. These carbs provide fiber and micronutrients important for digestion and energy regulation.
Incorporating Healthy Fats and Micronutrient-Rich Produce
Add nuts, seeds, olive oil, avocados, berries, spinach, kale, and broccoli to your meals. These foods support hormone balance, muscle repair, and immune function.
Safe and Effective Supplements to Support Muscle Gain
Supplements can fill gaps in nutrition but should never replace a balanced diet.
Whey Protein, Creatine, and BCAAs: Benefits and Usage
- Whey protein is a gold-standard supplement offering quick-digesting, high-quality protein. Learn more at Optimum Nutrition.
- Creatine monohydrate enhances muscle strength and endurance and is one of the most researched supplements. It helps regenerate energy during high-intensity exercise.
- BCAAs (branched-chain amino acids) can aid recovery and reduce muscle soreness, especially useful for training in a fasted state.
Multivitamins and Natural Supplements for Wellness
A multivitamin ensures you meet daily micronutrient needs, supporting energy metabolism and immune health. Natural supplements like turmeric or ginger have anti-inflammatory properties beneficial for recovery.
Special Considerations for Different Body Types and Lifestyles
Everyone’s body is unique. Adjusting the diet plan accordingly enhances success.
Diet Plans for Ectomorphs and Beginners
Ectomorphs (naturally thin individuals) often require a higher calorie surplus to gain muscle. Focus on nutrient-dense, calorie-packed meals, and don’t shy away from healthy fats and carbs. Beginners should prioritize balanced macro intake and gradual calorie increases while establishing consistent workout routines.
Plant-Based Diet Plans for Muscle Building
Plant-based eaters can meet their protein needs by combining different plant sources for complete amino acid profiles. Consider plant-based protein powders, nuts, and legumes heavily.
Sample 7-Day Meal Plan for Sustained Muscle Growth
Here’s a basic outline with portion sizes emphasizing proteins, carbs, and fats:
| Day | Meal 1 | Meal 2 | Meal 3 | Meal 4 | Meal 5 (Post Workout) | Meal 6 |
|—–|—————|—————–|——————-|——————|———————-|——————|
| 1 | Oatmeal + eggs | Greek yogurt + berries | Chicken breast + quinoa + veggies | Protein smoothie | Whey + banana | Salmon + sweet potato + greens |
| 2 | Scrambled tofu + whole grain toast | Cottage cheese + nuts | Lean beef + brown rice + broccoli | Hummus + carrots | Whey + oats | Tuna salad + avocado |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
Keep meals balanced, varied, and rich in nutrient-dense choices.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Your Diet Plan
Use tangible metrics to evaluate success.
Using Body Composition and Strength Gains as Metrics
Rather than focusing solely on the scale, track changes in muscle mass via body measurements, strength improvements, and how clothes fit. Adjust calories and macros as needed.
When to Consult a Nutritionist or Healthcare Professional
If progress stalls or you have specific health concerns, professional guidance can tailor the plan precisely. Registered dietitians specializing in sports nutrition are ideal.
Unique Insight: Harnessing Nutrient Timing with Mindful Eating for Enhanced Muscle Gain and Wellness
By paying attention to when and how you eat, particularly around workouts, you maximize nutrient absorption. Combine this with mindfulness—listening to hunger cues and eating slowly—to prevent overeating and foster a healthy relationship with food. This balanced approach supports not just muscle gains but overall well-being.
Key Points: Quick Takeaways
- Muscle protein synthesis is essential for muscle growth and requires adequate protein and calories.
- Maintain a controlled caloric surplus for lean muscle gain.
- Balance macronutrients: proteins (1.6-2.2 g/kg), carbs for energy, and healthy fats for hormone health.
- Meal timing is crucial: prioritize nutrient intake before and after workouts.
- Hydration supports muscle function and recovery; aim for about 3 liters daily.
- Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods from lean proteins, complex carbs, and healthy fats.
- Consider supplements like whey protein, creatine, and BCAAs as effective aids.
- Customize plans according to body type, diet preferences, and lifestyle.
- Track progress by body composition and strength, adjusting diet as needed.
- Incorporate mindful eating and nutrient timing for sustained muscle gain and wellness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the best diet plan for muscle gain at home without supplements?
A diet rich in whole, protein-dense foods like eggs, chicken, beans, and dairy paired with complex carbohydrates and healthy fats works well. Focus on hitting your protein and calorie goals with real foods and plan meals around your workouts.
2. How important is meal timing for muscle hypertrophy?
Meal timing enhances muscle gain by supplying nutrients when your muscles need them most—pre- and post-workout meals rich in protein and carbs optimize muscle protein synthesis and recovery.
3. Can plant-based diets support effective muscle gain?
Absolutely. Combining various plant protein sources ensures you get all essential amino acids. Supplementing with plant-based protein powders can also be helpful.
4. What role do healthy fats play in a muscle gain diet?
Healthy fats are crucial for hormone production, including those related to muscle growth. They also support overall health and reduce inflammation.
5. How much water should I drink daily to support muscle performance?
Aim for at least 3 liters per day, more if you engage in intense training or sweat heavily, alongside maintaining electrolyte balance for optimal muscle function.
Conclusion
Embarking on the best diet plan for muscle gain is about smart nutrition choices rather than quick fixes. By understanding muscle protein synthesis, maintaining a moderate caloric surplus, balancing macronutrients, and strategically timing your meals, you set yourself up for sustainable, lean muscle growth. Don’t overlook hydration and nutrient-dense whole foods—they fuel your workouts, recovery, and overall wellness.
Remember that every body is different, so tailor your approach and track your progress carefully. Incorporating safe, natural supplements can complement but should never replace a solid diet foundation. Finally, approach muscle gain with patience and mindfulness; it’s a journey toward better health and strength.
Ready to take the first step? Start planning your meals around these principles, fuel your workouts, and watch your muscles grow the healthy way!
For detailed meal planning tools and supplement info, I recommend visiting MyFitnessPal, Optimum Nutrition, and Orgain to access resources tailored to your muscle gain goals.

