Introduction: Why Fat Loss Matters for Health-Conscious Adults
Hey there! If you’re reading this, you’re probably weighing the options between weight training vs cardio for fat loss. Believe me, I’ve been there, trying to decode which method actually melts off the extra pounds and helps me feel strong and healthy. It’s no secret that fat loss isn’t just about looking good; it’s about improving overall wellness, enhancing energy, reducing disease risk, and living a fuller, more vibrant life.
In this article, I’m going to walk you through the ins and outs of both cardio and weight training when it comes to achieving fat loss naturally. We’ll dive into science-backed insights on metabolism, calorie burn, muscle preservation, and how combining these approaches can unlock the best results. As someone deeply invested in natural wellness, you’ll also find tips on balancing exercise with nutrition and lifestyle, making sustainable fat loss not just a goal, but a rewarding journey.
So, whether weight training or cardio has had you confused, this 3500-word guide will clear the fog. Let’s jump straight into understanding what truly works when it comes to fat loss, and how you can take charge of your health the smart way.
The Science Behind Fat Loss: Calories, Metabolism, and Energy Balance
How Calorie Deficit Drives Fat Loss
One thing I want to make crystal clear right off the bat is the fundamental principle driving fat loss—the calorie deficit. It’s simple: if you burn more calories than you consume, your body taps into stored fat for energy. This creates fat loss over time. No magic pill or workout can override this energy balance rule.
Your daily energy expenditure has several parts — basal metabolic rate (BMR), the calories your body burns to just keep you alive at rest; the thermic effect of food (TEF), the energy spent digesting food; and physical activity, including exercise and non-exercise movements. Creating a calorie deficit means tipping the scales by increasing energy expenditure (through exercise, movement) and/or moderating calorie intake.
Role of Metabolic Rate in Weight Reduction
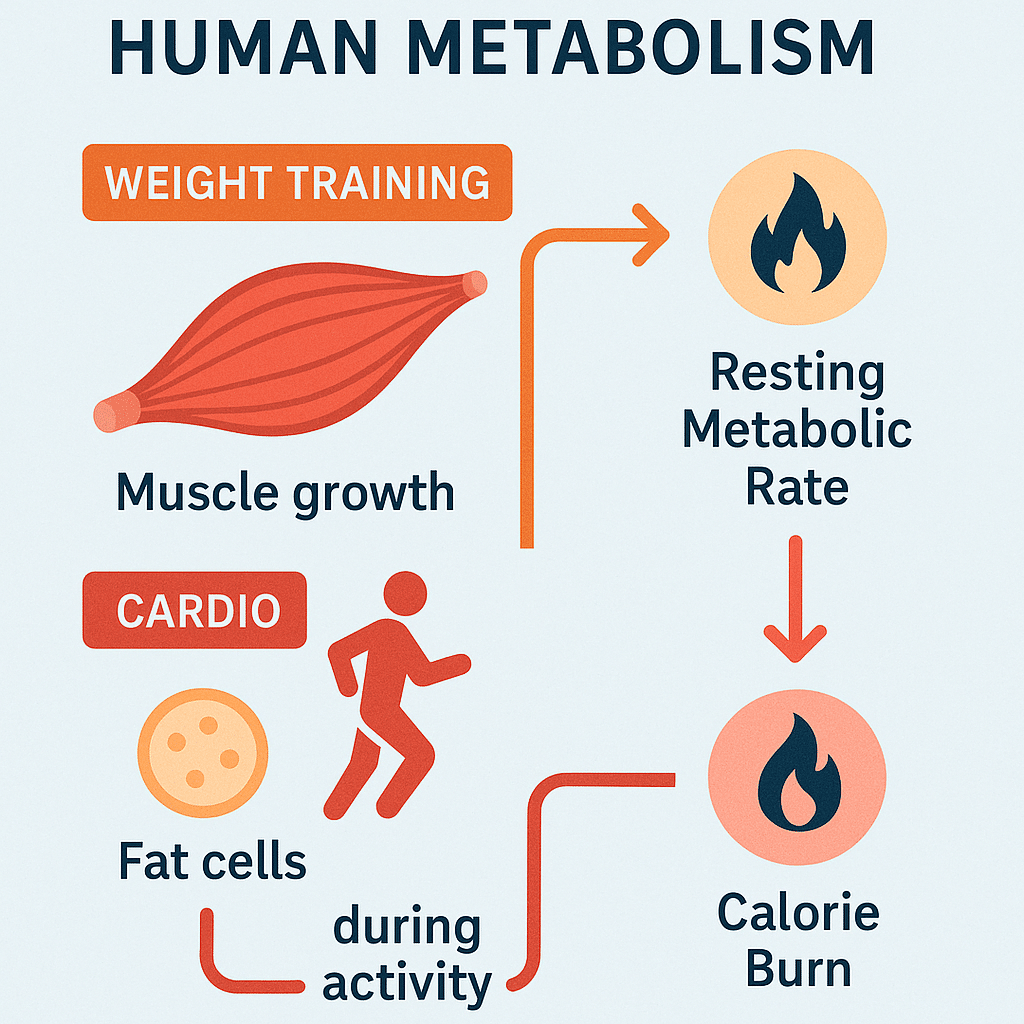
Now, here’s where exercise ties in. Metabolic rate isn’t a stagnant number; it fluctuates based on body composition and activity levels. Lean muscle mass plays a starring role here. The more muscle you have, the higher your resting metabolic rate — meaning you burn more calories even when doing nothing.
Both cardio and weight training impact your metabolism differently. While cardio burns calories during the activity, weight training boosts muscle — which can elevate metabolic rate over the long haul. Understanding this interplay is key to choosing the right fat loss strategy.
Cardio for Fat Loss: Mechanisms and Benefits
How Cardiovascular Exercise Burns Fat Efficiently
Cardiovascular exercise—think running, cycling, swimming, brisk walking—is a time-tested way to torch calories. When done consistently, cardio primarily uses fat and carbohydrates for fuel, helping reduce stored fat. Its effectiveness is partly due to the volume and intensity, which increase heart rate and energy expenditure.
Beyond calorie burn, cardio improves cardiovascular health by strengthening the heart and lungs, reducing blood pressure, and enhancing circulation. This synergy between heart health and fat loss is why cardio remains a favorite for anyone focused on natural wellness.
Types of Cardio: Steady-State, Interval, and HIIT for Fat Reduction
Not all cardio is created equal. You’ve got steady-state cardio—moderate effort done continuously (like a steady jog). Then there’s interval training—alternating between bursts of high intensity and recovery (think sprinting for 30 seconds, then walking).
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) mixes the best of both worlds. HIIT has gained massive popularity because it burns a ton of calories quickly and leads to excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC), a fancy term for the calorie burn that continues after you stop sweating. Studies show HIIT can effectively reduce fat, especially when combined with proper nutrition.
Cardiovascular Health and Fat Loss Synergy
Cardio doesn’t just burn fat; it improves metabolic health markers like insulin sensitivity and lipid profiles. Better heart health means your body functions more efficiently, supporting overall fat loss efforts. Plus, cardio helps manage stress, improves mood, and promotes better sleep—all critical for sustainable fat loss.
Weight Training and Fat Loss: Beyond Muscle Building
Resistance Training’s Effect on Metabolism and Lean Muscle Preservation
Shifting gears to weight training—also called resistance training—it’s often seen as pure muscle-building. But for fat loss? It’s a powerhouse tool. When you lift weights, your muscles face microscopic damage that prompts repair and growth, which demands additional calories.
Weight training preserves and even builds lean muscle mass during calorie deficits, which is crucial because maintaining muscle keeps your metabolic engine revving. This preservation is a huge win for natural wellness enthusiasts, as it contributes to a toned, healthy-looking physique and supports long-term fat loss.
Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption (EPOC) and Long-Term Calorie Burn
Ever heard of the “afterburn” effect? That’s EPOC in action. After weight training, your body works overtime to restore itself—replenishing oxygen, repairing muscles, balancing hormones—which uses extra energy.
In practical terms, EPOC means you continue to burn calories for hours (sometimes even up to 24-48 hours) after your workout. Weight training offers a sustained calorie burn advantage over steady-state cardio, making it an efficient method for fat loss.
Weight Training’s Role in Body Recomposition
One thing that trips people up is focusing only on weight loss versus body recomposition—losing fat while gaining or preserving muscle. Weight training emphasizes recomposition, fostering fat loss without sacrificing strength or muscle quality, which often happens with cardio-only routines.
For health-conscious adults keen on natural wellness, this balance means looking and feeling strong, not just lighter on the scale.
Comparing Calorie Burn: Weightlifting vs Cardio Workout Sessions
Exercise Intensity and Duration Impact
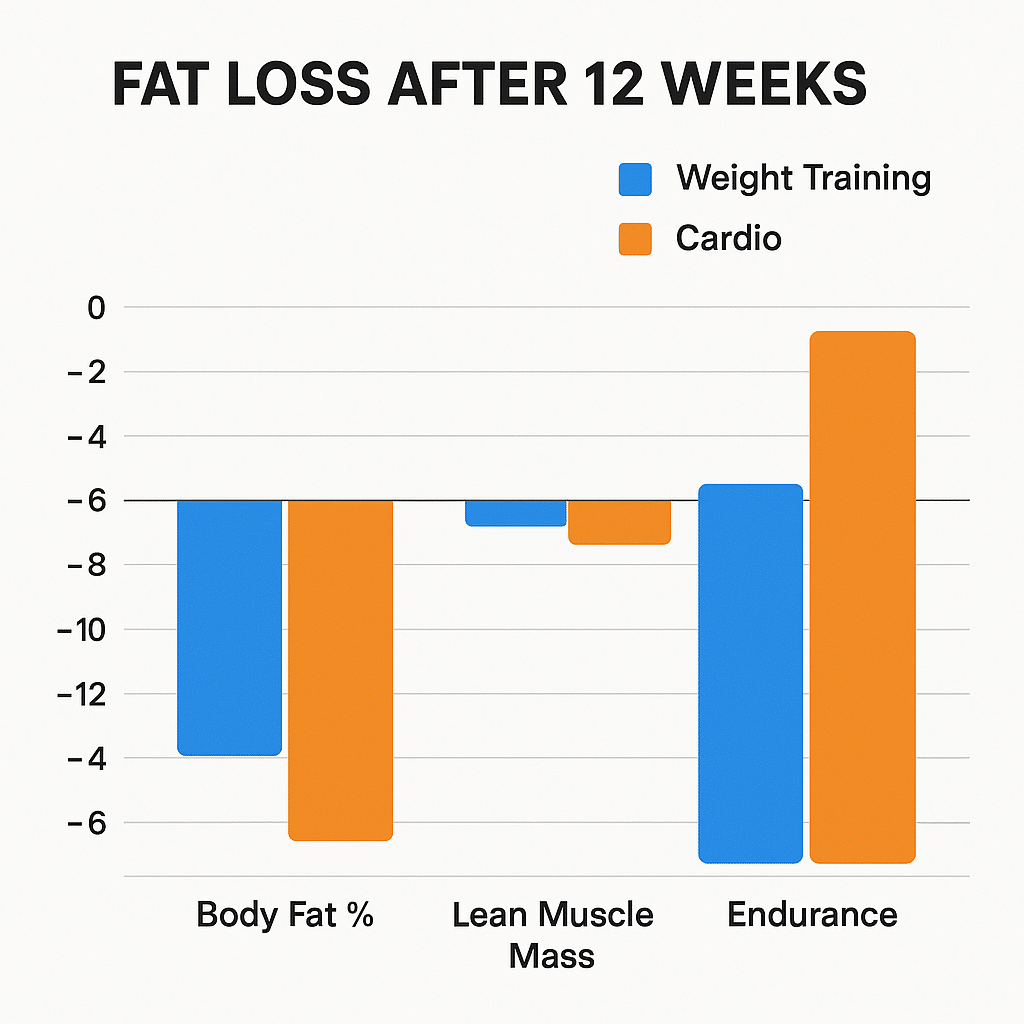
Let’s break down the numbers: cardio, especially running or cycling, burns more calories minute-for-minute than weightlifting. A 30-minute run might burn 300-400 calories, whereas a 30-minute weightlifting session may burn 150-250. However, these numbers don’t tell the full story.
Weightlifting’s post-exercise calorie burn and muscle-building benefits often tip the scales in its favor over time. Intensity matters too—vigorous weightlifting routines with minimal rest burn more total energy than casual lifting.
Fat Burning Efficiency of Running vs Weight Lifting
Running often ranks higher in immediate calorie burn, but weightlifting promotes a favorable hormonal environment for fat loss, including increased testosterone and reduced cortisol (stress hormone). Plus, weight training encourages fat loss with muscle retention, whereas steady-state cardio alone may cause muscle loss.
It’s a bit like comparing apples and oranges—they both have fat-burning perks with different mechanisms.
Combining Weight Training and Cardio for Optimal Fat Loss
How to Structure Your Exercise Routine for Maximum Fat Loss
Here’s the golden ticket: You don’t have to choose between weight training vs cardio for fat loss. The best results come when you combine both. I generally recommend starting your workout with weight training to recruit muscle when you’re fresh, then add cardio post-strength or on separate days.
Aim for 3-4 weight sessions weekly complemented by 2-3 cardio sessions (mix steady-state and HIIT). This combination maximizes calorie burn, muscle preservation, and heart health.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) as a Hybrid Strategy
HIIT cleverly blends cardio and strength by pushing intensity through exercises like kettlebell swings, burpees, or jump squats, alternating work and rest. It’s time-efficient, boosts EPOC massively, and builds muscle endurance.
For busy adults focused on natural wellness, incorporating HIIT can yield faster fat loss without spending hours in the gym.
Fat Loss and Muscle Preservation: Why Weight Training is Crucial
Preventing Muscle Loss during a Calorie Deficit
When cutting calories to lose fat, your body can mistakenly break down muscle along with fat if you’re not careful. That’s why weight training is essential—it signals your body to hold onto muscle because it’s needed.
Without weights, fat loss might come with muscle shrinkage, leading to a slower metabolism and sagging energy. Weight training protects your hard-earned muscle and supports a lean, sculpted look.
Metabolic Benefits of Maintaining Lean Muscle Mass
Muscle is metabolically active; the more you preserve, the higher your basal metabolic rate. A higher metabolism means sustained fat burning even on rest days. This is the key reason many experts suggest prioritizing resistance training during fat loss phases for the longevity of results.
Hormonal and Metabolic Effects: Cardio vs Weights
Impact on Appetite Regulation and Fat Storage Hormones
Exercise influences hormones like leptin (signals fullness) and ghrelin (triggers hunger). Weight training generally improves appetite regulation better than long, exhaustive cardio sessions, which can sometimes increase hunger, making fat loss trickier.
Furthermore, weight training tends to reduce insulin resistance, improving fat storage efficiency.
Cortisol, Testosterone, and Their Influence on Fat Loss
Excessive cardio, particularly prolonged endurance sessions, may elevate cortisol, the stress hormone which fosters fat storage, especially around the belly area.
In contrast, weight training boosts testosterone, a hormone supportive of muscle growth and fat loss. Balancing these hormones through a combined approach can optimize your fat loss outcomes.
Long-Term Sustainability and Exercise Adherence for Fat Loss Success
Psychological Benefits of Weight Training and Cardio
Fat loss isn’t just physical; mental health plays a huge part. Weight training often improves confidence and body image, while cardio enhances mood via endorphins. Personally, mixing both keeps my workouts fresh and manageable, making it easier to stick to my fat loss goals.
Creating a Lifestyle Routine for Consistent Fat Loss
Choosing an exercise style you enjoy boosts adherence. Natural wellness isn’t about punishing routines but creating habits that nurture your body and mind. By blending weight training and cardio, you can customize a schedule that fits your energy and lifestyle, leading to lasting fat loss.
Nutrition Synergy: Diet’s Role in Supporting Fat Loss from Exercise
Macronutrient Considerations for Weight Training and Cardio
Protein is king for anyone lifting weights—it supports muscle repair and satiety. Carbs fuel cardio sessions, providing energy for sustained performance. Fats support hormone balance. Balancing macros aligned with your workout type enhances fat loss.
Timing Nutrition Around Workouts to Maximize Fat Loss
Eating a protein-rich meal post-weight training supports muscle recovery. For cardio, easily digestible carbs pre-exercise boost endurance. Small, balanced meals spaced throughout the day can regulate blood sugar and optimize fat burning.
Special Considerations: Age, Gender, and Health Status in Choosing Fat Loss Exercise
Tailoring Exercise to Individual Metabolic and Physiological Needs
Older adults may benefit more from weight training to counter muscle loss associated with aging. Women may respond differently hormonally to cardio vs weights. Always consider health status and consult professionals to tailor routines to your unique needs for safest and most effective fat loss.
Addressing Common Myths about Cardio and Weight Training for Fat Loss
Myth: “Cardio is the only way to lose fat.” False. Weight training is equally important and often better for long-term results.
Myth: “Lifting weights makes you bulky.” Untrue for most adult women; weights help you tone and lean out.
Debunking these leads you closer to a balanced, realistic fat loss plan.
Practical Tips: Designing Your Personalized Fat Loss Workout Plan
Best Workout Routine for Fat Loss and Muscle Gain
A sample week might look like this:
| Day | Workout Type | Focus |
|———–|——————————|———————–|
| Monday | Weight Training (Full Body) | Muscle Building |
| Tuesday | Steady-State Cardio | Fat Burning |
| Wednesday | Weight Training (Upper Body) | Strength & Metabolism |
| Thursday | HIIT | Intense Calorie Burn |
| Friday | Weight Training (Lower Body) | Lean Muscle |
| Saturday | Light Cardio or Rest | Recovery & Heart Health |
| Sunday | Rest/Active Recovery | Wellness & Mobility |
Adjust reps, sets, and intensity based on fitness level. Monitor progress and tweak accordingly.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Your Regimen
Track body metrics, strength gains, mood, energy, and fat loss rate. If progress stalls, try increasing weights, altering cardio intensity, or revisiting nutrition. Stay patient — fat loss is a marathon, not a sprint.
Quick Takeaways
- Fat loss hinges on a calorie deficit—exercise enhances this by increasing energy expenditure and metabolic rate.
- Cardio burns more immediate calories and benefits heart health; HIIT offers a powerful fat-burning edge.
- Weight training preserves muscle, increases resting metabolic rate, and promotes long-term fat loss.
- Combining weight training with cardio yields the best fat loss and wellness results.
- Post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC) from weight training increases prolonged calorie burn.
- Weight training positively balances hormones supportive of fat loss; excessive cardio can elevate cortisol.
- Personalized, enjoyable routines improve adherence, ensuring sustainable fat loss.
Conclusion: The Balanced Approach — Why Weight Training vs Cardio is Not an Either-Or Choice
To wrap things up, I want to emphasize this crucial point: weight training vs cardio for fat loss is not an either-or choice—they’re complementary pillars of a smart fat loss journey. Cardio’s heart-pumping calorie blast combined with the metabolic muscle-building power of weight training create a one-two punch that accelerates fat loss while nurturing natural wellness.
Engaging in both exercises, supported by mindful nutrition and tailored to your body’s unique needs, sets you up for lasting transformation rather than quick fixes. This balanced approach spares you muscle loss, manages hormones, and maintains a healthy metabolism, which is essential for lifelong fat management.
So, take these insights, design your personalized routine, and step confidently into a healthier, stronger version of yourself. As someone committed to your natural wellness, remember: consistency, patience, and balance are your best friends on this journey—keep moving forward!
For more guidance on combining weight training and cardio, visit American Council on Exercise and certified programs like NASM to tailor your fat loss strategy.
FAQs
1. Does weight training burn more fat than cardio?
Weight training may not burn as many calories during the session as intense cardio, but it significantly boosts metabolism through muscle growth, leading to more fat burned over time.
2. Can cardio alone help lose belly fat?
Cardio helps reduce overall body fat, including belly fat, but combining it with weight training and proper diet is more effective for targeted fat loss and muscle preservation.
3. What is the best exercise for fat loss weight training or cardio?
Both have unique benefits; a mix of weight training to preserve muscle and cardio for calorie burn offers the most efficient fat loss results.
4. How does weight training affect metabolism and fat loss?
Weight training builds and preserves lean muscle, increasing resting metabolic rate, which helps you burn more calories even at rest, supporting effective fat loss.
5. Is high-intensity interval training (HIIT) effective for fat loss?
Absolutely! HIIT combines cardio and resistance elements, creating a powerful calorie burn during and after workouts, making it a time-efficient fat loss method.
This comprehensive guide should empower you with the knowledge and confidence to smartly combine weight training and cardio for the best fat loss outcomes—naturally and sustainably.

